Fleet Management Overview #
Fleet management refers to the process of managing a fleet of game servers. Because individual game server needs differ in configuration and scale, Pragma provides flexibility for game server allocation and orchestration. While most production-level games will use a third-party fleet management system, such as one included with a third-party game server, Pragma also offers the Pragma Fleet service to use during development.
Fleet management with a third party #
For managing game servers outside of the Pragma Fleet service, either in development or production
If you choose to manage your game server capacity outside of Pragma, whether in development or production, implement the following:
- Edit the findHostForGameInstance method. Have the Game Instance Host Plugin’s
findHostForGameInstancemethod returnnull. Use thefindHostForGameInstancemethod to generate partner tokens and integrate with your game server fleet manager in order to allocate a game server for this game instance. - Do not allow game servers to poll to report their capacity. To request game start data for a known game instance, use the
MatchApi.RequestStartGameSDK method - Prevent Pragma from spinning up Fleet service nodes. Add the following to your configuration files:
game:
core:
distributedServices:
FleetService:
nodeByInstanceId:
0: ~
Fleet management with the Pragma Fleet service #
For getting up and running in development
The Pragma Fleet service is responsible for processing game instance requests and coordinating with the game server provider to allocate game servers. Within this service, you can customize the Pragma Fleet Plugin, or use one of the pre-built plugins listed in the table below. The customizable Fleet Plugin provides an abstract interface for defining a game server fleet management model, and allows developers to manage game server capacity for fulfilling game instance requests. However, this method is not suitable for production.
The following pre-built Fleet service plugins are ready to use out-of-the-box:
| plugin | description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
DefaultFleetPlugin | Default implementation with one server pool using the default server management policy. This plugin does not allocate game servers. | Use as a placeholder while setting up your Pragma Engine |
LocalProcessFleetPlugin | Selects server pools based on game server version. | Use when running servers on a local development machine. See note below. |
PragmaNomadFleetPlugin | Selects server pools based on game server version. All server pools map to the default server management policy. | Use when running servers on Nomad in a development environment. |
MultiplayFleetPlugin | The Multiplay Fleet Plugin’s selectServerPool method uses a Multiplay regionId to determine a server pool. You map regionIds to Pragma gameServerZone values in the gameServerZoneToMultiplyRegionId block of your YAML configuration file. | Use when running servers using Unity’s Game Server Hosting (Multiplay), but NOT using their fleet management services. |
If you are using the LocalProcessFleetPlugin for local development only, consider using the LocalProcessGameServerProviderPlugin to make your local development more similar to your non-local environments.See Fleet Service Tasks for instructions on how to implement the various Fleet service methods.
You can view more details about the Fleet Plugin methods and their properties in the Fleet Service Reference topic.
Example fleet management flow #
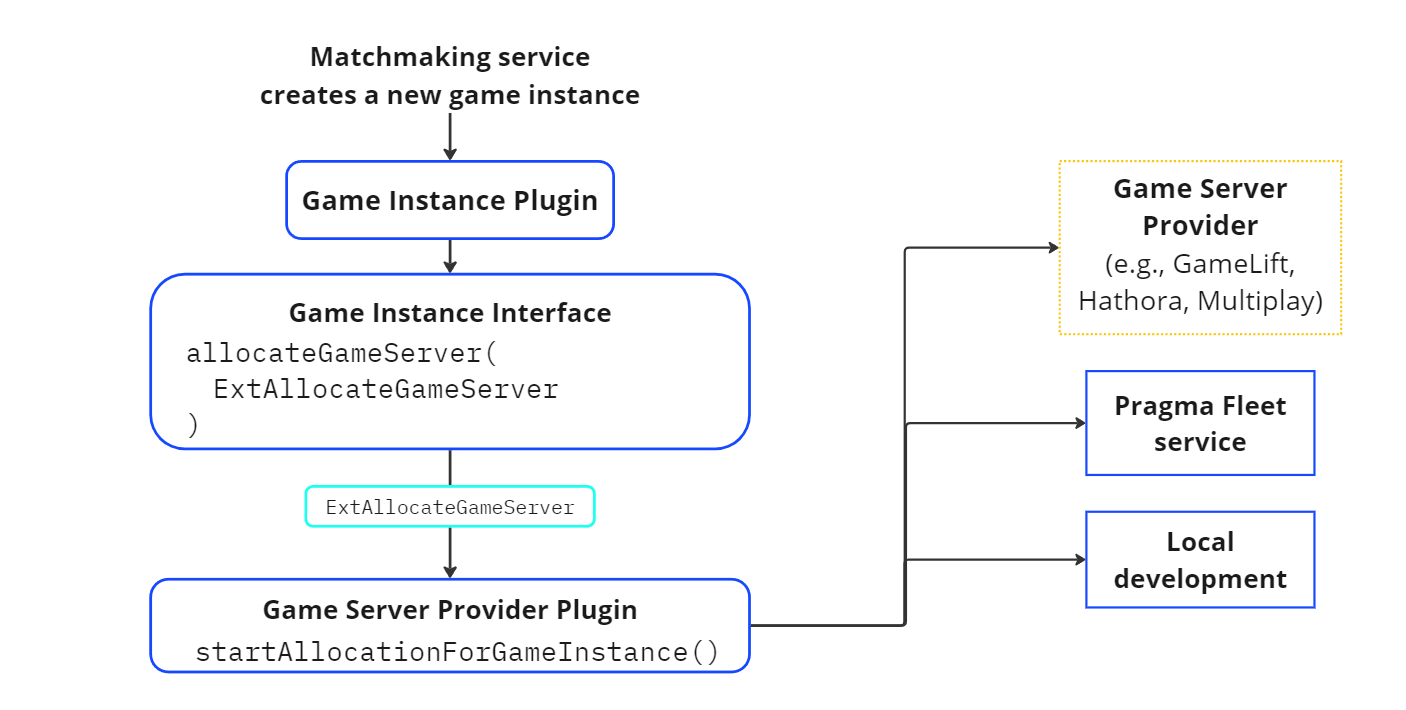
When the Matchmaking service finds a match, the service generates a NewGameInstance to send to the Game Instance service, and the Game Instance Plugin’s handleBackendCreateByMatchmakingRequest() method is called. You can customize this method to prepare data that needs to be sent to the game server fleet manager to aid in allocation.
By default, handleBackendCreateByMatchmakingRequest() calls GameInstance.allocateGameServer() with a default ExtAllocateGameServer payload, but you can call GameInstance.allocateGameServer() from any Game Instance Plugin method. When allocateGameServer() is called, your Game Server Provider Plugin implementation’s startAllocationForGameInstance() method is invoked.
In environments not using the Pragma Fleet service:
Use the startAllocationForGameInstance() method to integrate with your game server fleet manager to allocate a game server for this game instance, and provide game instance data and connection tokens. Further fleet management tasks will be handled by the third-party fleet management provider.
In environments using the Pragma Fleet service:
Use the startAllocationForGameInstance() method to send ExtAllocateGameServer containing relevant NewGameInstance information to the Fleet service. With this information, the Fleet service puts in an allocation request as well as select an appropriate server pool for this new game instance. The allocation request is placed in a queue to wait for a game server it can be allocated to.
Meanwhile, the Pragma Engine internal capacity manager automatically reviews the allocation request queue to determine whether or not a game server’s reported capacity can accommodate the request. If there is insufficient capacity, the Fleet service allocates additional capacity on the Pragma side and returns a list of game server IDs for you to use when spinning up additional game servers to support the pending allocation requests.
Every time a game server reports its available capacity, the Fleet service finds queued allocation requests assigned to the game server’s server pool. Based on the server’s reported available capacity, the Fleet service provides the game server with a list of game instance IDs ready to run.