Fleet Service Key Concepts #
The Fleet service is responsible for managing game instance allocation to game servers. Game servers report their capacity for game instances to the Fleet service, and receive in response a list of new game instances to run.
To facilitate this capability, you can partition your game server fleet according to two facets: server pools and server pool management policies .
Server Pools #
Server pools allow you to segment your fleet of game servers by common features, such as game server zone, game server version, and custom values such as game mode. Using server pools, the Fleet service can determine what server pool a given game instance should be associated with, ensuring the game instance finds an appropriate game server to run on.
Server pool implementation can be useful if you have game servers that each run only one type of game (e.g., one game server runs PvP casual, another runs PvP competitive). You could also use server pools to segment your servers by geographic region or expected workload.
Each game server maps to one server pool, which in turn maps to one server pool management policy to inherit general server pool settings. You can define additional custom data, such as game version, in an individual pool’s ExtServerPool payload to further inform the game server allocation process.
Server Pool Management Policies #
Server pool management policies define capacity characteristics that you can apply to one or more pools of game servers. Server pool management policy configuration options include:
- Number of games allowed to run on a single game server
- Minimum and maximum game capacity allocated at all times
- Maximum time a game server can take to start before allocation fails
- Interval at which a game server should report its capacity
- Number of reporting heartbeats that can be missed before allocation fails
- Maximum time the platform will wait for capacity to resolve for a game instance before ejecting it
For a list of all values, see the Fleet Service Components topic’s Server Pool Management Policy Configuration table.
Example Game Flow #
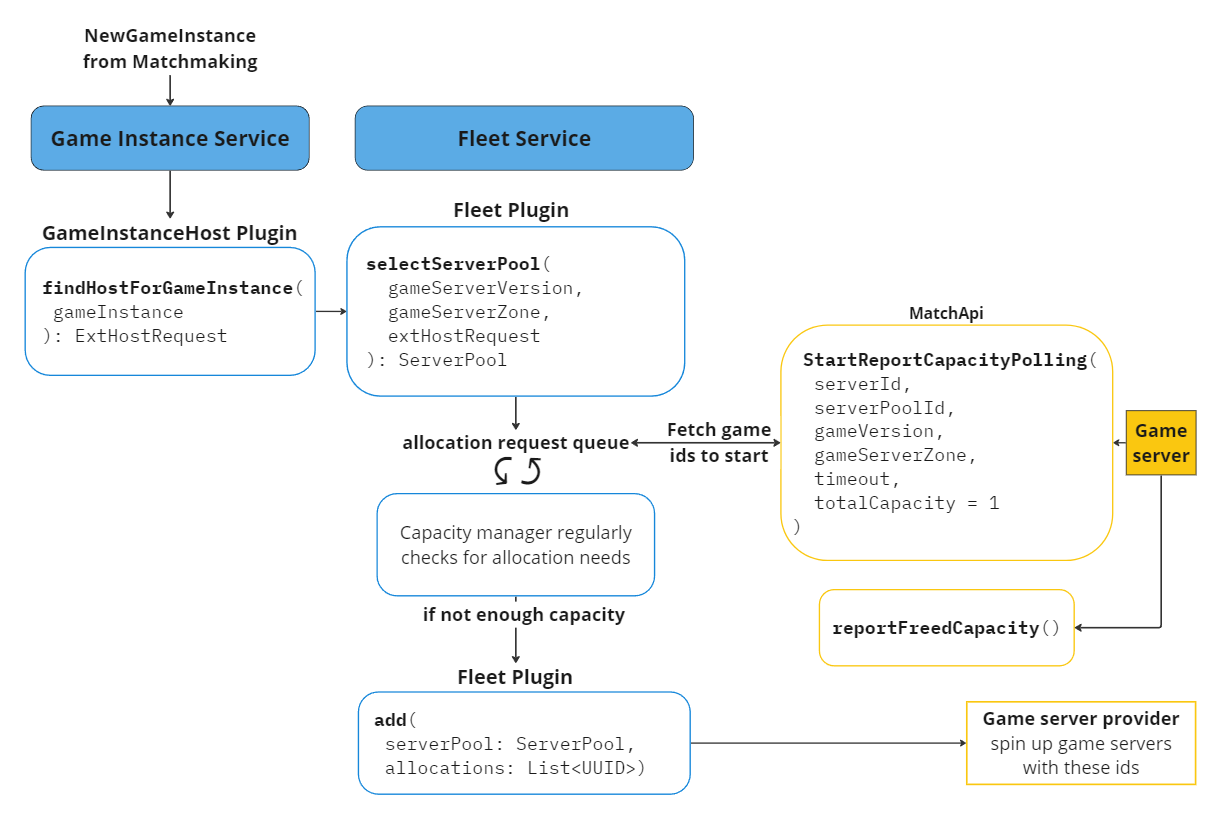
When the Matchmaking service finds a match, the service generates a NewGameInstance to send to the Game Instance service. The Game Instance service generates an ExtHostRequest containing relevant NewGameInstance information to send to the Fleet service. With this information, the Fleet service puts in an allocation request as well as selects an appropriate server pool for this new game instance. The allocation request, is placed in a queue to wait for a game server it can be allocated to.
Meanwhile, the Pragma Engine internal capacity manager automatically reviews the allocation request queue to determine whether or not a game server’s reported capacity can accommodate the request. If there is insufficient capacity, the Fleet service allocates additional capacity on the Pragma side and returns a list of game server IDs for you to use when spinning up additional game servers to support the pending allocation requests.
Every time a game server reports its available capacity, the Fleet service finds queued allocation requests assigned to the game server’s server pool. Based on the server’s reported available capacity, the Fleet service provides the game server with a list of game instance IDs ready to run.