Log into the Platform #
In this section, we’ll be logging in with the configured SDK using a test user.
Write the code #
For this example, we will put code in a PragmaManager MonoBehaviour. Create a Scripts folder in your Assets folder. Create a new C# script named PragmaManager and open it.
Add the following code to
PragmaManager1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69using UnityEngine; public class PragmaManager : MonoBehaviour { public Pragma.Player Player { get; private set; } private void Awake() { // The Pragma Runtime is automatically initialized on first retrieval. var runtime = Pragma.Runtime.Get(); runtime.Config.ConfigData.backendAddress = "http://127.0.0.1:10000"; runtime.Config.ConfigData.protocolType = Pragma.ProtocolType.WebSocket; runtime.Config.ConfigData.gameClientVersion = "GameServerVersion1"; // This returns the first Player if available, or creates it. The Runtime is the source of truth for Player objects. Player = runtime.Player(); // Add listeners connection-related events as desired. Player.OnConnected += HandleConnected; Player.OnDisconnected += HandleDisconnected; Player.OnDegraded += HandleDegraded; Player.OnRecovered += HandleRecovered; } public void LogIn() { Player.LogIn(Pragma.Account.IdProvider.Unsafe, "test01", HandleLoggedIn); } public void LogOut() { Player.LogOut(HandleLoggedOut); } private void HandleLoggedIn(Pragma.Result result) { if (result.IsFailure) { Debug.LogErrorFormat("Pragma -- Login failed: {0}", result.ErrorCode); return; } Debug.Log("Pragma -- Logged in."); } private void HandleLoggedOut() { Debug.Log("Pragma -- Logged out."); } private void HandleConnected() { Debug.LogFormat("Pragma -- Connected. PragmaId: {0}", player.PragmaId); } private void HandleDisconnected() { Debug.Log("Pragma -- Disconnected."); } private void HandleDegraded() { Debug.Log("Pragma -- Degraded."); } private void HandleRecovered() { Debug.Log("Pragma -- Recovered."); } }
Link the login script to a button #
Open your project the Unity editor.
Right click in an empty part of the Hierarchy pane on the left side, click Create Empty, and name the
GameObjectPragmaManager.Drag the
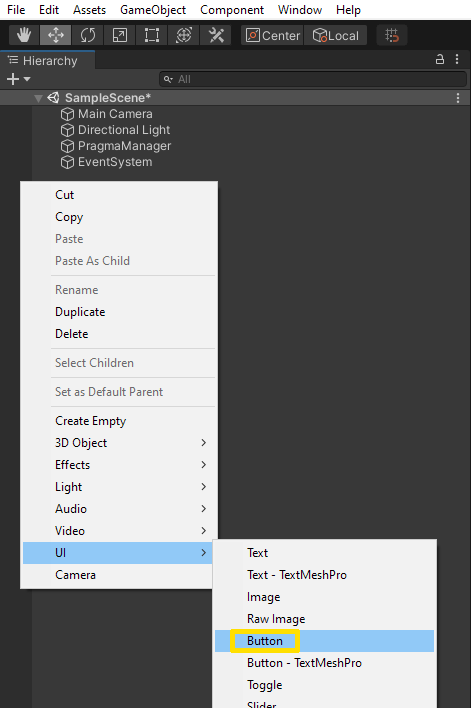
PragmaManager.csscript onto thePragmaManagerGameObject.Right click in the Hierarchy pane and select UI then Button.
Expand the Button object in the Hierarchy pane and select Text.
In the Inspector pane, find the Text box with the default text of
Button. Rename it by typingLogin.In the Hierarchy pane, click on the Button object.
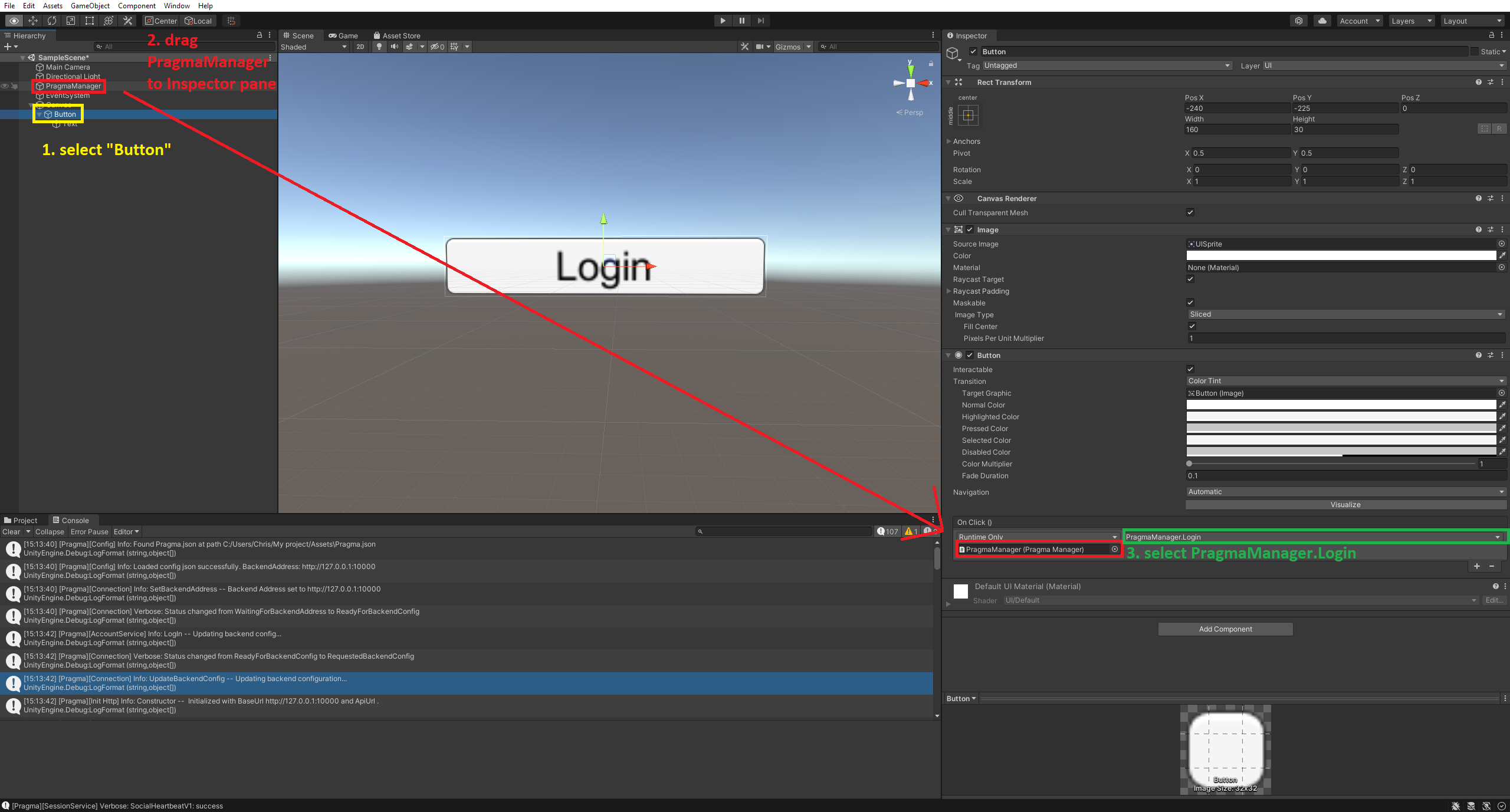
In the On Click (), select the + sign, and drag
PragmaManagerfrom the Hierarchy pane onto None (Object) in the Inspector pane. Click No Function and select PragmaManager, then Login().
Try it out! #
- Run Pragma Engine via one of the following methods.
Once the engine has started successfully, it prints the message [main] INFO main - Pragma server startup complete.
In Unity, click play, then click the Login button to connect to your locally running Pragma Engine instance.
Return to your Unity project and scroll through the console messages and you should see a line like
Pragma -- Logged in..
The Unsafe login method is disabled by default in production. It is ‘unsafe’ because it has no password or other security measures!
Once logged in, you can call other Pragma API calls like this: Player.*Service Name*.Action().